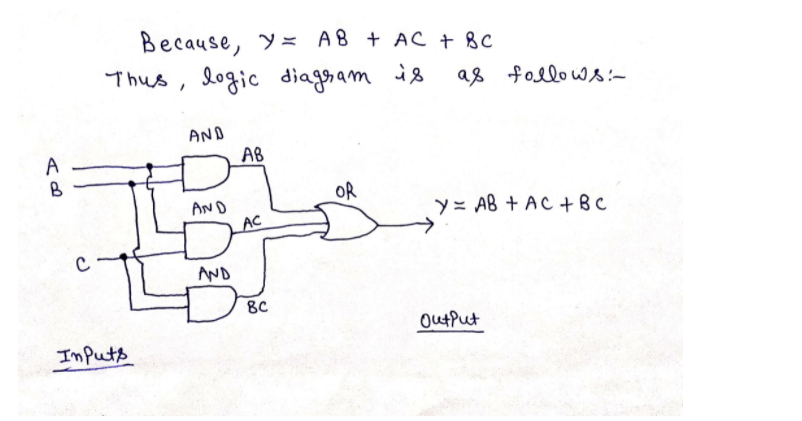
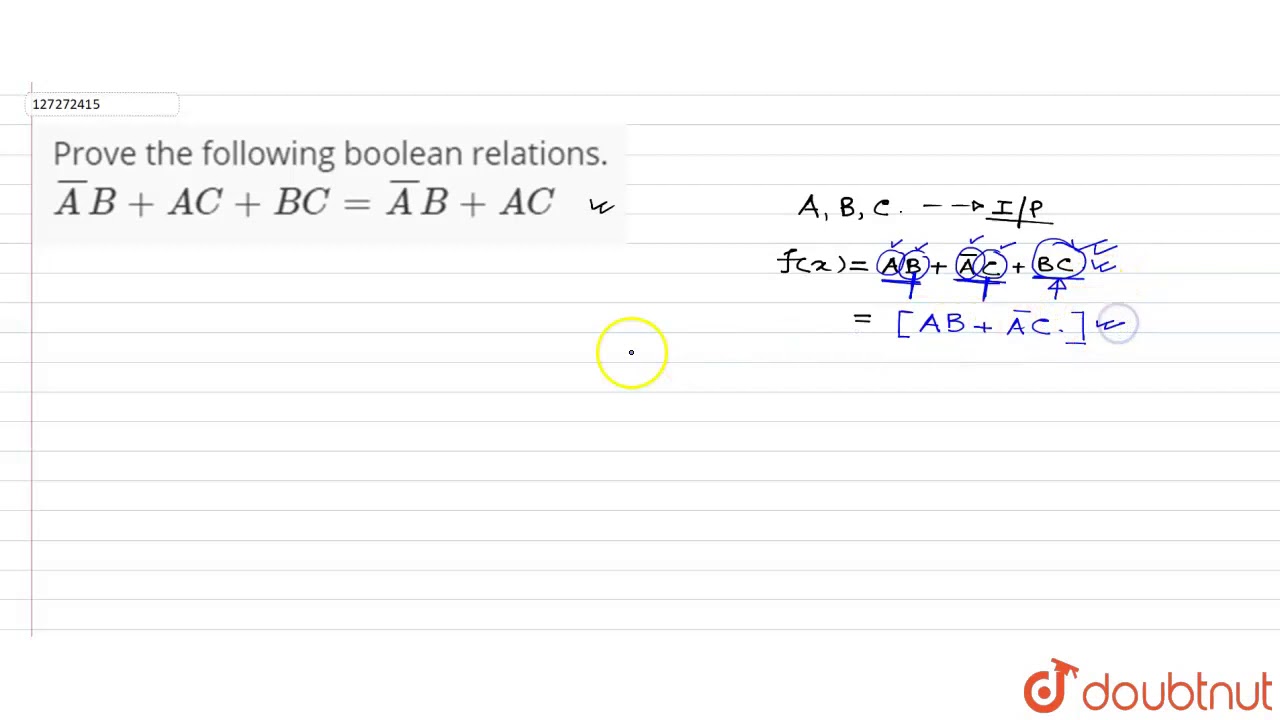
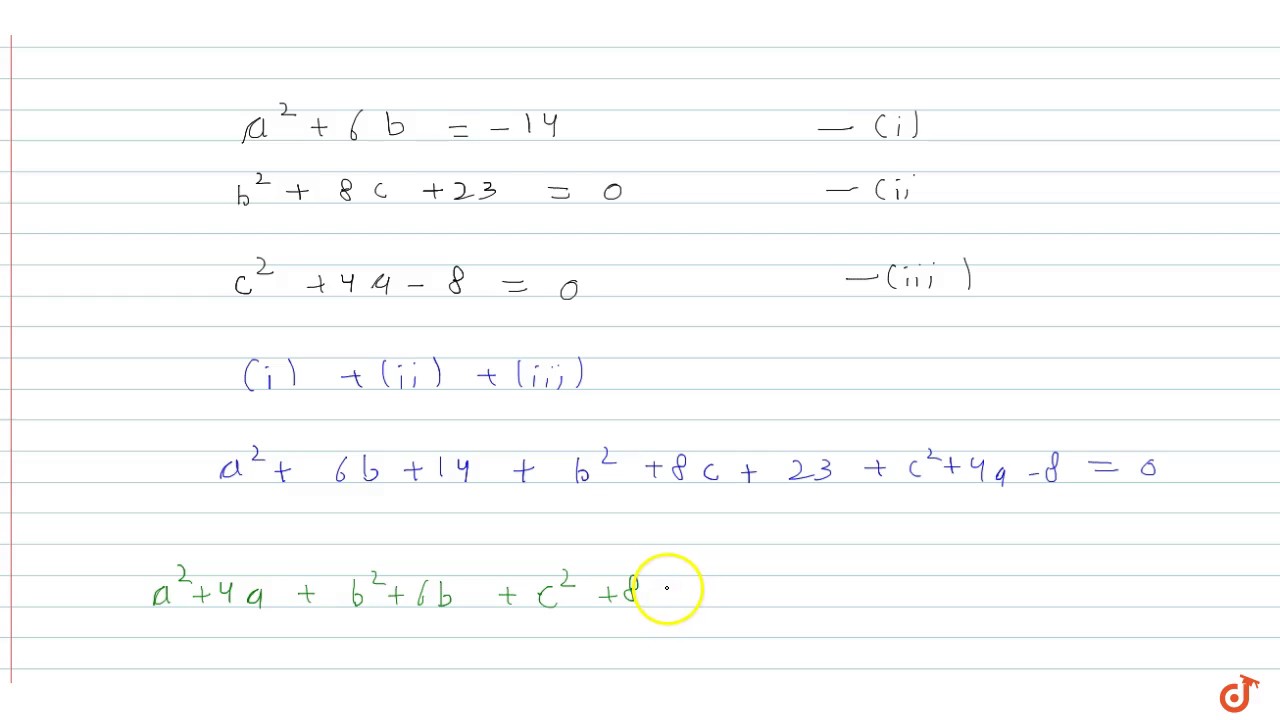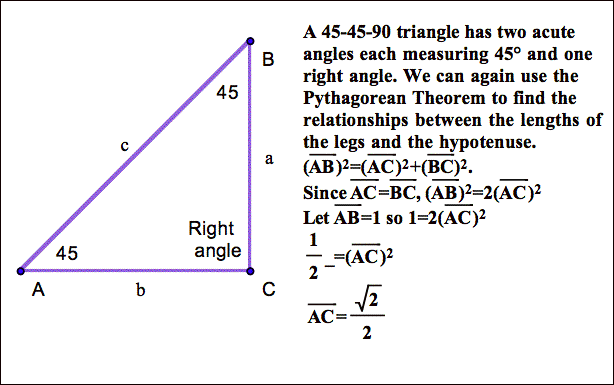ABC is a triangle in which `AB = AC and D` is a point on AC such that `BC^2 = AC xx CD`.Prov - YouTube

SOLVED: Expression a + 0 =a a+b=b+a Dual a . 1 =0 ab ba a+(b+c)=latb)tc a(bc) = (abc a + bc = Ka+ ba +c) a(b +c) = ab + ac a+6 =

A is Invertible and AB = AC Prove B = C If A is Singular find 2 Matrices where AB =AC P 2-5-6 - YouTube
In ∆ABC, if AC is greater than AB, then prove that AC AB is less than BC, AC BC is less than AB and BC AB is less than AC.